Containerization with Docker and Kubernetes is revolutionizing how full-stack developers build, deploy, and manage applications. This powerful combination allows for faster development cycles, enhanced scalability, and improved reliability. Imagine building and deploying an application with pinpoint accuracy, independent of infrastructure nuances. This is the power of containerization. Traditional methods of deployment often involve complex and time-consuming processes, leading to slower release cycles and potential instability. This article will explore how containerization with Docker and Kubernetes effectively addresses these challenges for full-stack projects. We’ll delve into the core concepts, practical examples, and real-world use cases to illustrate how these technologies can significantly streamline the application lifecycle. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of containerization, from setting up a Docker environment to deploying applications using Kubernetes. We’ll also touch upon best practices and troubleshooting tips to enhance efficiency and avoid common pitfalls.
Understanding Containerization with Docker
What is Containerization?
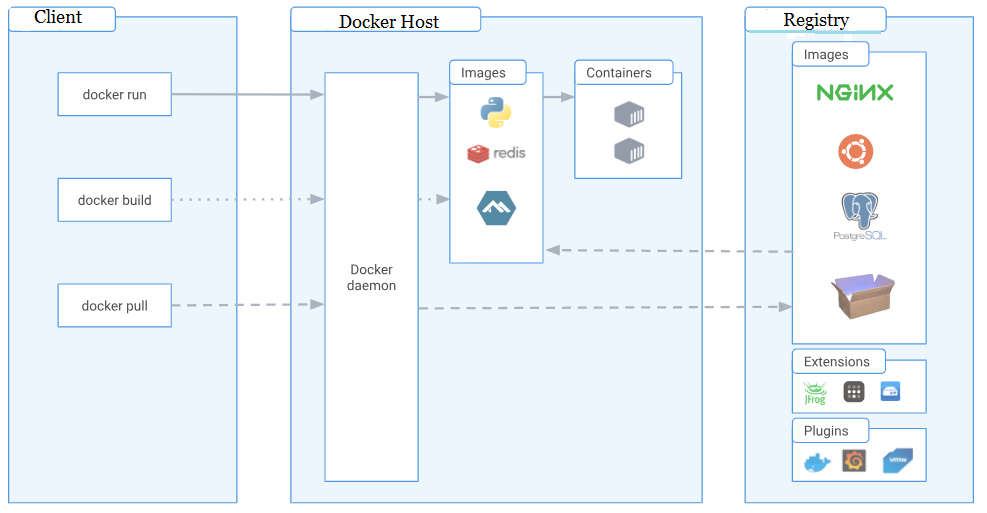
Containerization is a lightweight virtualization method that packages software with all its dependencies into a single unit called a container. This containerized application runs consistently regardless of the underlying infrastructure. Think of it as a portable software package that includes everything needed to run—dependencies, libraries, and the application itself. Docker is the most popular containerization platform, simplifying the process of packaging, deploying, and managing containers.
Docker’s Role in Containerization
Docker provides a standardized way to create, run, and manage containers. Its core component, the Docker Engine, handles the container runtime and provides functionalities for interacting with containers. Docker images are the blueprints for containers. These images are built from Dockerfiles, which specify the steps required to create the container’s environment. This approach allows for rapid application deployment across various environments. Docker simplifies complex dependencies management. Developers can package their applications and dependencies together in a container and deploy it without worrying about compatibility issues between different environments.
Introduction to Kubernetes
Container Orchestration with Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source platform for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It’s a container orchestration tool designed to manage the lifecycle of containerized applications across multiple servers. Kubernetes facilitates managing large-scale container deployments and eliminates many of the manual processes involved in container management. In essence, Kubernetes manages the entire container ecosystem, ensuring applications run consistently and reliably across clusters.
Benefits of Using Kubernetes
One of the major advantages of using Kubernetes is its ability to scale applications dynamically. As demand increases, Kubernetes automatically adds or removes containers to maintain the desired application performance. This automatic scaling enhances efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Kubernetes also facilitates deployment across multiple servers, eliminating the difficulties of maintaining consistent application performance across different environments. Kubernetes also provides a robust mechanism for managing containerized applications, including features like service discovery, load balancing, and automated rollouts and rollbacks.
Related Post : Scaling Full-Stack Applications for Growing User Bases.
Building and Deploying Applications with Docker and Kubernetes
Practical Application Deployment
Let’s look at how developers can leverage this technology for practical applications. Assume a full-stack application—imagine an e-commerce platform for example. The application likely has front-end, back-end, and database components. Docker can bundle all these components into separate containers, making the deployment and scaling process seamless.
Real-world Use Cases
Consider a hypothetical e-commerce site experiencing high traffic during peak seasons. Kubernetes, with its ability to scale dynamically, can easily handle this surge. Kubernetes can automate the process of adding or removing containers as needed, ensuring quick response times and preventing service disruptions during periods of high demand. This approach ensures a smooth customer experience while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Best Practices and Considerations
Optimizing for Performance and Reliability
Several best practices exist for containerizing applications with Docker and Kubernetes. Choosing the right image size is crucial for performance, and developers should use optimized images to reduce container size. Similarly, minimizing dependencies is critical for efficient application deployment. Developers need to optimize containers to run efficiently.
Security Considerations
Security must be a top concern when employing containerization technologies. Regularly updating images, maintaining strict access controls, and performing security audits are crucial for mitigating vulnerabilities. Secure configurations are paramount to safeguarding sensitive data and preventing malicious attacks. Proper security measures are vital for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of data in a containerized environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing Deployment Challenges
One common issue when deploying applications in a containerized environment is compatibility problems between different containerized components. For example, misconfigurations in the Dockerfile or Kubernetes deployment manifests might lead to unexpected behavior. Thorough testing and debugging are crucial for identifying and rectifying these problems early in the development process. A meticulous approach to testing will prevent unnecessary problems later in the deployment lifecycle.
Leveraging Logs and Metrics
Kubernetes provides comprehensive logging and monitoring features to help developers troubleshoot problems and improve application performance. Observing logs and metrics enables developers to identify potential bottlenecks or errors in real time, optimizing application behavior. Logging and monitoring provide essential insights into the performance and stability of the containerized application, allowing proactive issue resolution.
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
FAQ Answers
In conclusion, containerization with Docker and Kubernetes empowers full-stack developers to build, deploy, and manage applications more efficiently. By abstracting away the complexities of infrastructure, these tools allow for quicker development cycles, improved scalability, and increased reliability. Leveraging this technology streamlines the entire application lifecycle, making it easier to deliver high-quality applications. To dive deeper into containerization, consider enrolling in online courses or workshops focused on Docker and Kubernetes. These resources can further enhance your skills in deploying and managing applications in a containerized environment.